Where Should Wall Ties Be Placed
Understanding the Purpose of Wall Ties
Wall ties play a fundamental role in maintaining the integrity of cavity walls. Their main function is to connect the internal and external leaf of a cavity wall, ensuring stability and load distribution across the structure.
Wall ties are vital in preventing problems such as wall bowing, cracking, or even collapse. The materials used to manufacture them—typically stainless or galvanized steel—are designed to resist moisture ingress and corrosion, making them a reliable long-term solution. Used extensively in both new builds and refurbishments, these components are a critical part of the Masonry Connectors and Wall Ties range.
Correct Placement Based on Wall Construction
Wall tie placement largely depends on the type of wall being constructed. Whether it's a timber frame or a traditional cavity masonry wall, the positioning must follow specific standards to ensure compliance and performance.
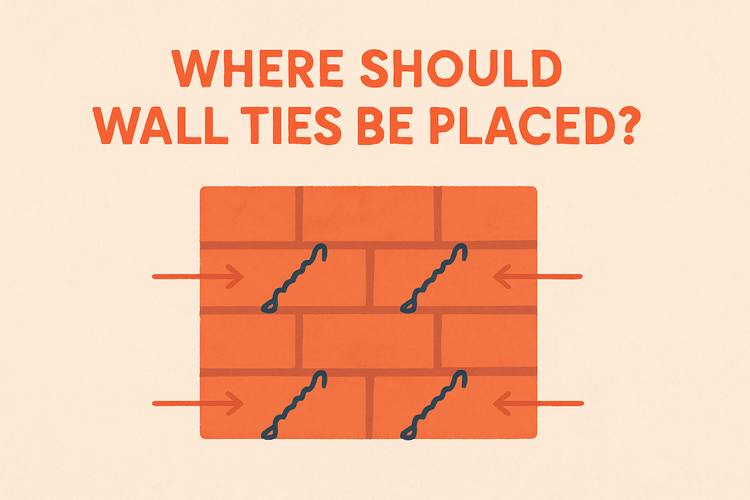
For cavity walls, ties are typically placed horizontally every 900mm and vertically every 450mm. This grid pattern ensures even load transfer and keeps both leaves of the wall tied consistently. Wall corners and structural openings such as windows and doors demand additional ties placed within 225mm of the edge at intervals not exceeding 300mm. These placements are crucial for managing stress points within the structure.
In timber frame construction, wall ties designed to connect timber to external brickwork must be selected appropriately. Proper embedment in the mortar joint and correct spacings are key to performance and safety. Wall ties that form part of the Timber Frame Connectors collection are specifically designed for these unique requirements.
Factors Influencing Wall Tie Spacing
Spacing requirements for wall ties may vary based on environmental exposure and wall height. Higher buildings or those in severe weather conditions need tighter spacing due to increased load factors.
Wind load is a critical consideration. In areas exposed to high winds—especially coastal or elevated locations—wall ties might need to be installed more frequently than the standard grid pattern. Ties placed more densely help counteract the lateral loads exerted by strong wind pressures. Products from the High Wind ties & timber connectors category provide added reinforcement suitable for such harsh conditions.
Masonry type can also affect spacing. Lightweight blockwork or less stable materials typically require more frequent tie placement. The density and conductivity of the material contribute to decisions about tie length and corrosion protection, maintaining safety and thermal performance.
Installation Techniques for Optimal Performance
Proper installation of wall ties ensures their long-term effectiveness and compliance with building regulations. A poor installation can lead to voids in the wall, bridging of the cavity, or corrosion risks that compromise safety.
Wall ties must be carefully embedded into fresh mortar beds, with a minimum penetration depth—typically 50mm—into each leaf of the masonry. The drip feature of the tie should point downward and be correctly positioned in the middle of the cavity to prevent water from transferring across the wall cavity. The use of appropriate screws, fixings, and shields ensures compatibility with the surrounding construction materials.
Maintaining consistent alignment during installation is critical. Misalignment or incorrect orientation can reduce load-sharing capacity and even cause premature failure. It's also vital to cover or protect wall ties during construction pauses to avoid contamination or premature corrosion.
Choosing the Right Wall Tie for Your Project
Not all wall ties are created equal. Selecting the correct type depends on various project-specific factors, including the cavity width, type of wall, and exposure category.
For example, butterfly ties are often used in timber frame constructions, while double triangular ties are favored in poured concrete walls. For more unusual applications, wall starter profiles may be necessary to initiate ties that branch off existing masonry walls. Always consult national building regulations and manufacturer's guidelines to ensure you're using an approved wall tie for your environment.
Also, consider the material and coating. Stainless steel offers the best durability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for long-term or high-exposure projects. Galvanized versions may be sufficient for internal or sheltered applications but offer less corrosion protection over time, especially in damp climates. For enhanced performance across all wall applications, explore the options in the Masonry Connectors and Wall Ties collection.
